Debt-to-Income Ratio Explained: Why It Matters for Homebuyers
Kari Cooper
When you're ready to buy a home, it's important to know what lenders look at when deciding if they'll give you a mortgage. One big thing they consider is your Debt-to-Income (DTI) ratio. This blog will explain what DTI is, why it's important for homebuyers, and how you can handle it to boost your chances of getting that mortgage approval.
Skip to
What is the Debt-to-Income Ratio?
Types of DTI Ratios
Why the DTI ratio matters?
How to calculate your DTI ratio
Ideal DTI ratios for homebuyers
Strategies to Improve Your DTI Ratio
The Impact of DTI on Mortgage Options
Managing DTI Ratio for Self-Employed Homebuyers
The Role of Credit Score with Respect to DTI Ratio
How Student Loans Affect Your DTI Ratio
The Effect of DTI Ratio on Refinancing
How Major Life Events Affect Your DTI Ratio
The Future of DTI Ratios in Mortgage Lending
Key Takeaways
FAQs
What is the Debt-to-Income Ratio?
Lenders use something called the Debt-to-Income (DTI) ratio to see if you can handle your monthly payments and debts. They figure it out by dividing all your monthly debt payments by how much money you make each month. Then they show it as a percentage.
Types of DTI Ratios
- Front-End Ratio: This looks at how much of your income goes towards paying for your home, like your mortgage, property taxes, insurance, and any association fees.
- Back-End Ratio: This considers all your monthly debts, including things like credit card bills, car payments, student loans, and any other loans you have, along with your housing costs
Why the DTI Ratio Matters?
- Lender’s View: Lenders consider your DTI to assess lending risk. A lower ratio signals good debt management and increases the likelihood of timely mortgage payments.
- Affordability Check: Your DTI guides lenders in determining your borrowing capacity. A lower ratio expands your borrowing potential, enabling you to qualify for larger loans.
- Loan Approval Rules: Lenders enforce maximum DTI ratios for loan approvals. Conventional loans favor ratios below 36%, while FHA loans may accept ratios up to 43%.
- Interest Rates and Deals: A lower DTI can unlock better loan terms, such as reduced interest rates. Lenders perceive lower-ratio borrowers as less risky, leading to more favorable terms.
How to Calculate Your DTI Ratio
- List Your Debts: Write down all regular debts like rent, credit card bills, car payments, student loans, and other loans you pay monthly.
- Calculate Your Total Income: Add up your income before taxes, including your salary, bonuses, and any investment returns.
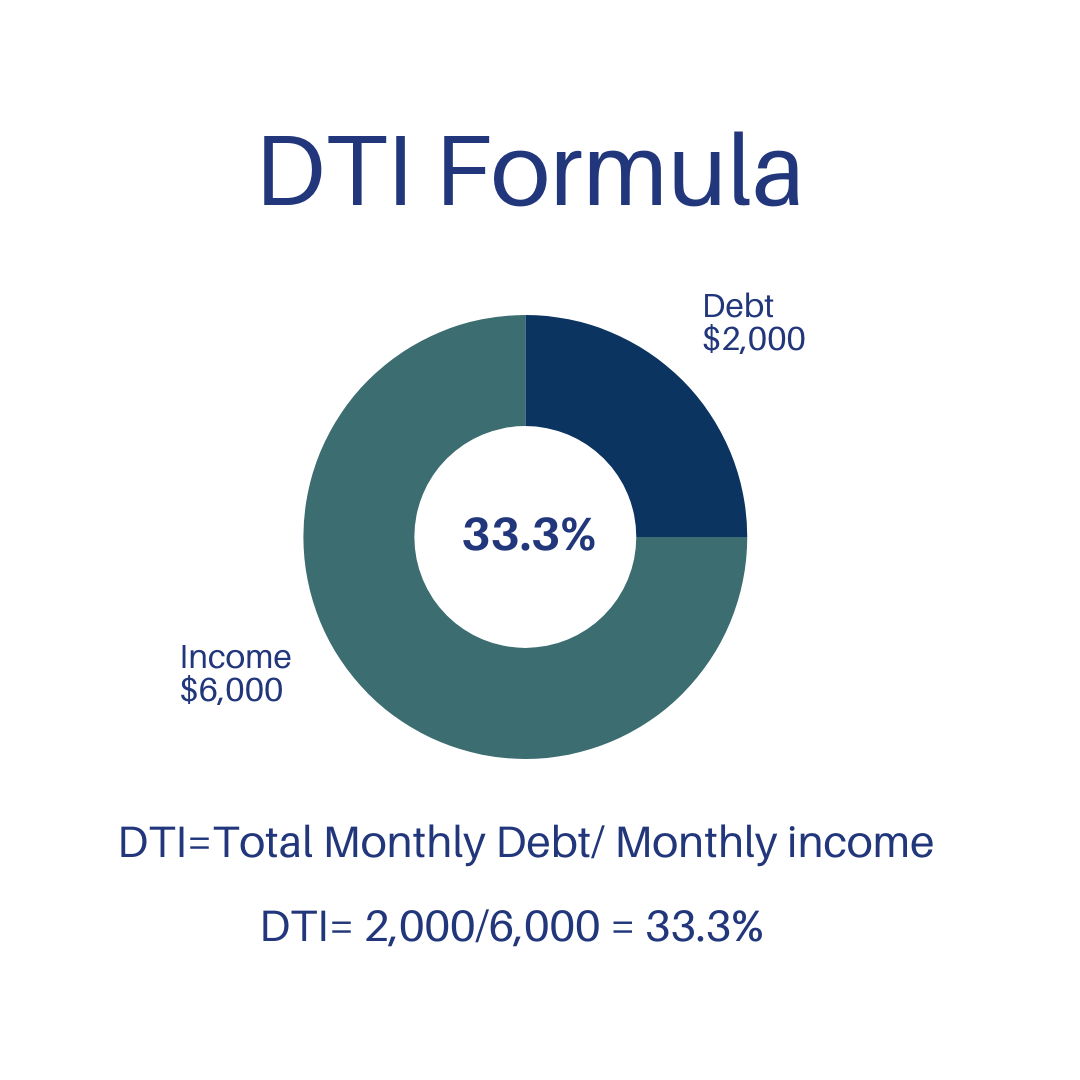
- Do the Math: Divide your total monthly debts by your gross monthly income. Then multiply the result by 100 to get your DTI percentage. For instance, if your monthly debts are $2,000 and your income is $6,000, your DTI would be:
- List Your Debts: Total monthly debt payments = $2,000
- Calculate Your Total Income: Gross monthly income = $6,000
- Do the Math: DTI Ratio = (Total monthly debt payments / Gross monthly income) * 100 = ($2,000 / $6,000) * 100 = 0.3333 * 100 = 33.33%
So, in this example, the Debt-to-Income (DTI) ratio would be 33.33%.
Ideal DTI Ratios for Homebuyers
While the ideal DTI ratio can vary depending on the lender and loan type, here are some general guidelines:
- Conventional Loans: Preferably below 36%, but can go up to 43% with strong compensating factors.
- FHA Loans: Up to 43%, but can be higher in certain situations.
- VA Loans: Typically up to 41%, but some lenders may accept higher ratios.
- USDA Loans: Generally up to 41%.
Strategies to Improve Your DTI Ratio
- Increase Your Income: Consider taking on additional work, asking for a raise, or finding new income streams to boost your gross monthly income.
- Pay Down Debts: Focus on paying off high-interest debts first. Reducing your total monthly debt payments will directly lower your DTI ratio.
- Avoid New Debt: Refrain from taking on new debt, such as personal loans or credit card purchases, before applying for a mortgage.
- Refinance Existing Debt: Look into refinancing options for existing loans to lower your monthly payments.
- Debt Consolidation: Consolidating multiple debts into a single loan with a lower interest rate can reduce your monthly payments and simplify your debt management.
The Impact of DTI on Mortgage Options
Your DTI ratio can affect the types of mortgage loans you qualify for:
- Conventional Loans: These loans typically require a lower DTI ratio. Borrowers with a higher ratio may need to provide a larger down payment or seek a co-signer.
- FHA Loans: More lenient on DTI ratios, making them an attractive option for first-time homebuyers or those with higher debt levels.
- VA Loans: Designed for veterans and active military members, these loans have flexible DTI requirements but still favor lower ratios.
- USDA Loans: Available for rural and suburban homebuyers, these loans also consider DTI but may offer leniency based on other factors.
Calculate your DTI ratio today using our DTI Calculator Template and get closer to your dream home.
Managing DTI Ratio for Self-Employed Homebuyers
Self-employed individuals often face unique challenges in managing their DTI ratio due to fluctuating incomes and complex financial structures. Here are some tips for self-employed homebuyers:
- Document Income Thoroughly: Maintain comprehensive records of all income sources, including tax returns, bank statements, and profit/loss statements.
- Separate Personal and Business Finances: Keep your personal and business accounts separate to provide a clearer picture of your financial situation.
- Stabilize Your Income: Show consistent income over at least two years. Lenders prefer stability and predictability in earnings.
Minimize Business Debt: Reduce outstanding business debts where possible to improve your overall DTI ratio.
The Role of Credit Score with Respect to DTI Ratio
While the DTI ratio is crucial, your credit score also plays a significant role in the mortgage approval process. Here’s how these two factors interact:
- Credit Score Impact: A high credit score can offset a slightly higher DTI ratio. Lenders may be more willing to approve a loan if your credit history is strong.
- Combined Risk Assessment: Lenders use both DTI and credit score to assess your risk profile. A low DTI and high credit score together improve your chances of favorable loan terms.
- Improving Credit Score: Paying down debts not only improves your DTI ratio but also boosts your credit score by lowering your credit utilization ratio.
How Student Loans Affect Your DTI Ratio
Student loans can significantly impact your DTI ratio, particularly for younger homebuyers. Here’s what to consider:
- Monthly Payments: Include your student loan payments in your DTI calculations. Even deferred loans must be factored in if they will become due within the year.
- Repayment Plans: Consider income-driven repayment plans to lower your monthly payments and improve your DTI ratio.
- Loan Forgiveness Programs: If you are eligible for loan forgiveness programs, this can positively impact your long-term debt picture.
The Effect of DTI Ratio on Refinancing
If you’re looking to refinance your mortgage, your DTI ratio will still play a crucial role. Here’s how:
- Refinancing Requirements: Similar to obtaining a new mortgage, lenders will evaluate your DTI ratio when considering a refinance application.
- Lower Rates and Payments: Refinancing to a lower interest rate can reduce your monthly payments, thereby improving your DTI ratio.
- Cash-Out Refinancing: Be cautious with cash-out refinancing, as it increases your total debt and can negatively impact your DTI ratio.
How Major Life Events Affect Your DTI Ratio
Major life events such as marriage, divorce, or having children can affect your DTI ratio. Here’s how to manage these changes:
- Marriage: Combining incomes with your spouse can improve your DTI ratio, but their debts will also be included in calculations.
- Divorce: Divorce can complicate your DTI ratio, particularly if you are responsible for alimony or child support payments.
- Growing Family: Having children can increase your monthly expenses, affecting your DTI ratio. Budgeting and planning for these changes are essential.
The Future of DTI Ratios in Mortgage Lending
The mortgage industry continually evolves, and so do the guidelines around DTI ratios. Here’s a look at potential future trends:
- Technology and Automation: Advances in technology may lead to more sophisticated tools for assessing borrower risk, potentially considering a broader range of financial behaviors beyond the traditional DTI ratio.
- Economic Conditions: Economic shifts, such as changes in employment rates or housing market conditions, can influence lender policies on acceptable DTI ratios.
- Regulatory Changes: Government regulations and policies can impact how lenders evaluate DTI ratios. Staying informed about these changes is crucial for prospective homebuyers.
Key Takeaways
- Mortgage Approval Factors: Knowing what lenders consider when approving a mortgage is crucial for aspiring homeowners.
- Importance of DTI Ratio: The Debt-to-Income (DTI) ratio is a significant factor lenders use to assess your ability to manage monthly payments and repay debts.
- Types of DTI Ratios: Front-End Ratio focuses on housing-related debt, while Back-End Ratio includes all monthly debt obligations.
- Why DTI Matters: Lenders use DTI to evaluate risk, determine affordability, approve loans, and set interest rates and terms.
- Calculating Your DTI: Calculate your DTI by dividing total monthly debt payments by gross monthly income, then multiply by 100 to get the percentage.
FAQs
Q) What is the maximum DTI ratio to qualify for a mortgage?
A) While it varies by lender, a DTI ratio below 36% is generally preferred. Some loans, like FHA loans, may accept ratios up to 43% or higher in specific situations.
Q) Can I still get a mortgage with a high DTI ratio?
A) Yes, but you may need to provide additional documentation, make a larger down payment, or pay a higher interest rate.
Q) How can I lower my DTI ratio quickly?
A) Paying off high-interest debts, avoiding new debt, and increasing your income are effective strategies.
Q) Does my spouse’s debt affect my DTI ratio if we apply jointly?
A) Yes, when applying for a joint mortgage, both applicants' debts and incomes are considered.
Q) Is the DTI ratio the only factor lenders consider?
A) No, lenders also consider your credit score, employment history, and the amount of your down payment.
Conclusion
Understanding and managing your Debt-to-Income ratio is essential for homebuyers looking to secure a mortgage. By keeping your DTI ratio low, you can improve your chances of loan approval, secure better interest rates, and ensure that you can comfortably afford your new home. Take proactive steps to manage your debt, increase your income, and make informed decisions throughout the home-buying process. If you have more questions or need personalized advice, don't hesitate to reach out to a mortgage professional.
If you need assistance in managing your DTI ratio,
Contact Us today.
Our experts at Austin Capital Mortgage are here to guide you every step of the way.
Related Links
List of Services
-
Mortgage 101: How Does A Mortgage Work?List Item 1
Buying a property is a huge investment, and your mortgage will likely be your biggest debt. Don't go in blind! Here's what you need to know about mortgages before taking the plunge:
-
How to Get Pre Approved? A Step by Step Guide to Mortgage Pre ApprovalList Item 2
Buying a home is a big decision and one of the most significant financial commitments you’ll ever make. To make the process smoother, getting preapproved for a mortgage is essential.
-
Understanding Closing Costs: What to Expect When Buying a Home Write a description for this list item and include information that will interest site visitors. For example, you may want to describe a team member's experience, what makes a product special, or a unique service that you offer.
List Item 3

